The power of meditation to overcome depression
In the quest for practical approaches to combatting depression, the power of meditation to overcome depression has gained significant attention. This introduction delves into the myriad benefits of incorporating meditation into strategies for overcoming depression. Depression, a complex mental health condition, necessitates comprehensive solutions, and recent research suggests that meditation offers a promising avenue for intervention.
By examining how meditation impacts the mind, emotions, and neurological processes, we can uncover valuable insights into its potential as a complementary tool in the treatment of depression. This exploration sets the stage for understanding how the practice of meditation may contribute to alleviating the symptoms of depression and fostering mental well-being.
The effects of depression on mental well-being.
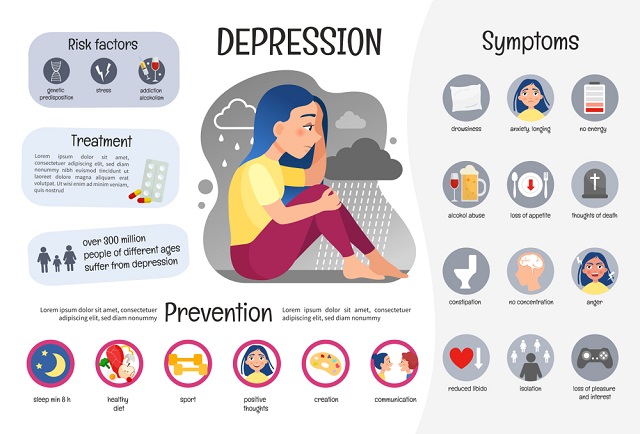
Depression, often described as a pervasive and persistent mood disorder, significantly impacts mental health by disrupting various aspects of an individual’s well-being. To comprehend the significance of meditation in addressing depression, it’s crucial to delve into the intricate web of factors contributing to this condition.
Complex Nature of Depression
Depression is not a monolithic experience; it is a nuanced and complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. At its core, depression involves alterations in brain chemistry, neurotransmitter imbalances, genetic predispositions, and life experiences. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of depression is essential in developing effective strategies for coping and recovery.
Symptoms and Manifestations
The symptoms of depression extend beyond mere feelings of sadness. Individuals grappling with depression often experience persistent low mood, a profound sense of hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities they once enjoyed. Physical symptoms, such as changes in appetite and sleep patterns, further contribute to the overall toll on mental health.
The Impact on Cognitive Functioning
Depression significantly affects cognitive functioning and has the potential to disrupt concentration, memory, and decision-making capabilities. The mind becomes trapped in a cycle of negative thoughts, often characterized by self-doubt and self-criticism. This cognitive distortion further perpetuates the emotional distress associated with depression.
Social and Interpersonal Consequences
Depression extends beyond the individual’s internal world, influencing social and interpersonal dynamics. Relationships may strain as the affected individual may withdraw from social interactions, finding it challenging to articulate their emotional struggles. This isolation can deepen the sense of loneliness and exacerbate the impact on mental health.
The Role of Stigma
The stigma surrounding mental health issues, including depression, adds layer of complexity. Societal misconceptions and prejudices can hinder individuals from seeking help, exacerbating the duration and severity of depressive episodes. Understanding and dismantling these stigmas are crucial steps in creating a supportive environment for those affected by depression.
Chronic Nature and Recurrence
Depression is often characterized by its chronic nature and the potential for recurrence. Individuals who have experienced a depressive episode are at an increased risk of facing subsequent episodes. This chronicity underscores the need for comprehensive and sustained approaches to managing and mitigating the impact on mental health.
Gaining a deep understanding of depression and its multifaceted impact on mental health lays the foundation for exploring holistic approaches to treatment. Meditation, as we will further explore, emerges as a promising tool in addressing the diverse challenges posed by depression, offering a complementary avenue for fostering mental well-being.
The science behind meditation: How it affects the brain
Meditation, often regarded as an ancient practice rooted in various cultural and spiritual traditions, has garnered increasing attention from the scientific community. Recent research has delved into the neurological underpinnings of meditation, unraveling how this practice can induce structural and functional changes in the brain. Understanding the science behind meditation provides valuable insights into its potential as a therapeutic tool, particularly in the context of mental health, including depression.
Neuroplasticity
At the core of the science behind meditation is the concept of neuroplasticity. This refers to the brain’s remarkable ability to reorganize itself, forming new neural connections throughout life. Meditation, particularly mindfulness meditation, has been associated with increased neuroplasticity. Regular practice stimulates the growth of neurons and the formation of new neural pathways, contributing to changes in brain structure and function.
Impact on Brain Structure
Studies using neuroimaging techniques like MRI scans have demonstrated that meditation can lead to structural changes in key brain regions. The hippocampus, associated with memory and learning, and the amygdala, involved in emotional processing, have shown increased gray matter density in regularly meditating individuals. These structural changes are linked to improvements in memory, emotional regulation, and overall mental well-being.
Functional Connectivity
Meditation influences not only the structure but also the functional connectivity of the brain. Available MRI studies have revealed alterations in the connectivity between different brain regions, especially those involved in attention, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. These changes contribute to the observed improvements in cognitive functions and emotional resilience associated with meditation.
Mindfulness and the Default Mode Network
The default mode network (DMN) is a network of brain regions active when the mind is at rest and not focused on the outside world. The DMN is often associated with self-referential thinking and mind-wandering. Meditation, particularly mindfulness practices, has been shown to modulate the activity of the DMN. This modulation is linked to a reduced tendency for the mind to wander into negative thought patterns, a common characteristic of depression.
Neurotransmitter Regulation
Meditation has been found to influence the production and activity of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons. For instance, the practice has been associated with increased serotonin levels, crucial in mood regulation. This neurotransmitter modulation is particularly relevant in the context of depression, where imbalances are often observed.
Stress Response and the Amygdala
The amygdala, a key player in the brain’s stress response system, changes meditation. Regular practice has been linked to a reduction in the size and activity of the amygdala, leading to a diminished stress response. This is significant in the context of depression, as chronic stress is a contributing factor to the development and worsening of the condition.
In summary, the science behind meditation provides compelling evidence of its transformative effects on the brain. These neurological changes not only shed light on the mechanisms through which meditation may alleviate the symptoms of depression but also emphasize its potential as a proactive and preventive approach to maintaining optimal mental health.
Using meditation as a tool in managing depression
As our understanding of the science behind meditation deepens, an increasing number of individuals, including mental health professionals, are turning to meditation as a valuable tool in the comprehensive management of depression. Incorporating meditation into a treatment plan for depression offers a holistic approach, addressing not only the symptoms but also the underlying factors contributing to this complex mental health condition.
Stress Reduction and Cortisol Regulation
One of the primary ways meditation supports individuals with depression is through stress reduction. Chronic stress is a significant contributor to the onset and exacerbation of depression. Meditation techniques, such as mindfulness and focused breathing, activate the body’s relaxation response, decreasing the production of stress hormones, including cortisol. By fostering a state of calm, meditation helps break the cycle of chronic stress often associated with depression.
Cultivating Mindfulness and Interrupting Negative Thought Patterns
Mindfulness, a central component of many meditation practices, involves paying non-judgmental attention to the present moment. For individuals with depression, this means observing thoughts without becoming entangled in them. By cultivating mindfulness, meditation interrupts the cycle of negative thought patterns, a hallmark of depressive thinking. This shift in awareness provides individuals with a valuable tool to manage the cognitive aspects of depression.
Emotional Regulation and Resilience
Depression often involves heightened emotional reactivity and difficulties in regulating emotions. Meditation, particularly mindfulness meditation, empowers individuals to develop emotional resilience. By becoming more aware of their emotions and learning to observe them without immediate reaction, individuals can navigate the emotional challenges associated with depression more effectively. This enhanced emotional regulation contributes to a more stable and positive mood.
Enhancing Self-Awareness and Empowerment
Meditation fosters self-awareness, a crucial component in managing depression. Through regular practice, individuals gain insight into their thoughts, triggers, and emotional responses. This heightened self-awareness empowers individuals to make conscious choices and implement positive life changes. It provides a sense of agency and control, countering the feelings of helplessness often associated with depression.
Improved Sleep and Physical Well-Being
Depression commonly disrupts sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and exacerbating overall well-being. Meditation has been associated with improvements in sleep quality and duration. The calming effects of meditation contribute to better sleep hygiene, positively impacting physical health and energy levels. Improved sleep, in turn, can break the cycle of fatigue and low mood often experienced by individuals with depression.
Incorporating Meditation into Treatment Plans
Mental health professionals increasingly recognize the potential of meditation in managing depression. Integrating meditation into a comprehensive treatment plan, alongside therapy and medication when appropriate, offers a well-rounded approach to addressing the multifaceted nature of depression. Individuals are encouraged to work with healthcare providers to tailor a meditation practice that aligns with their unique needs and preferences.
Using meditation as a tool for managing depression harnesses the transformative power of this ancient practice. By addressing stress, cultivating mindfulness, regulating emotions, and enhancing self-awareness, meditation offers a proactive and empowering approach to complement traditional therapeutic interventions. As part of a holistic strategy, meditation can contribute significantly to the journey of managing and overcoming depression.
Techniques for incorporating meditation into your daily routine
Establishing a regular meditation practice can be a transformative way to nurture mental well-being in a world filled with constant demands and distractions. Incorporating meditation into your daily routine doesn’t necessarily require hours of seclusion; rather, it involves finding practical and sustainable ways to infuse moments of mindfulness into your day. Here are some techniques to seamlessly integrate meditation into your daily life:
Start with Short Sessions
If you’re new to meditation, begin with short sessions to make it more manageable. Even five to ten minutes of meditation can yield benefits. Find a quiet space, sit comfortably, and focus on your breath or a guided meditation. As you become more accustomed to the practice, you can gradually extend the duration.
Mindful Morning Routine
Incorporate meditation into your morning routine to set a positive tone for the day. This can include a brief meditation session upon waking or practicing mindfulness while engaging in morning activities such as showering, brushing your teeth, or having breakfast. Mindful awareness during routine tasks cultivates a sense of presence from the start.

Lunchtime Mindfulness Breaks
Use your lunch break as an opportunity for a mindfulness pause. Find a quiet spot, whether a park bench or a quiet corner in your office, and engage in a short meditation. This can help alleviate midday stress and refresh your mind for the tasks ahead.
Mindful Walking
Transform your daily walk into a mindfulness practice. Pay attention to each step, the sensation of your feet connecting with the ground, and the rhythm of your breath. Walking mindfully incorporates meditation into your routine and adds a refreshing dimension to your physical activity.
Breath Awareness Throughout the Day
Use your breath as an anchor throughout the day. Take moments to pause and focus on a few conscious breaths, especially during transitions between activities. This simple technique can be practiced discreetly and helps bring your attention back to the present moment.
Evening Wind-Down
Create a calming evening routine with meditation to unwind from the day’s demands. Whether guided meditation, deep breathing exercises, or a simple mindfulness reflection, incorporating meditation into your evening routine can signal to your body and mind that it’s time to relax.
Technology-Assisted Meditation
Leverage technology to support your meditation practice. Numerous meditation apps offer guided sessions, making integrating meditation into your daily routine easy. Set aside a specific time each day to use these resources, whether during a commute or before bedtime.
Mindful Breathing Before Sleep
Practice mindful breathing as part of your bedtime routine. Lie down comfortably, close your eyes, and focus on your breath. This can help calm the mind, promote relaxation, and improve the quality of your sleep.
Create Rituals
Establish rituals around your meditation practice to make it a consistent part of your routine. This could involve lighting a candle, playing soft music, or using specific cushions or chairs. Rituals signal to your brain that it’s time for a mindful pause.
Be Flexible and Gentle with Yourself
Recognize that life can be unpredictable, and it’s okay if your meditation routine varies. Be flexible and gentle with yourself. The essence of meditation is not perfection but a commitment to returning to the practice regularly.
Incorporating meditation into your daily routine is a personal journey. Experiment with different techniques, find what resonates with you, and gradually weave moments of mindfulness into the fabric of your day. As you cultivate a consistent practice, you may discover that even brief moments of meditation contribute to a profound sense of calm and balance in your daily life.
Seeking professional guidance and support alongside meditation
While meditation can be a powerful tool in managing mental health, including conditions like depression, it is essential to recognize that it is not a replacement for professional guidance and support. Combining meditation with professional mental health care can create a comprehensive and practical approach to well-being. Here’s why seeking professional advice is crucial alongside a meditation practice:
Comprehensive Assessment: Mental health professionals, such as therapists and psychiatrists, are trained to conduct comprehensive assessments. They can evaluate the specific nuances of your mental health, identify underlying issues contributing to depression, and tailor a treatment plan to address your unique needs. This personalized approach is crucial for effective and sustainable progress.
Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning: Depression can manifest in various forms, and its causes may differ from person to person. Mental health professionals can provide an accurate diagnosis, distinguishing depression from other mental health conditions. With this clarity, they can develop a targeted treatment plan that may include a combination of therapy, medication, and complementary practices such as meditation.
Therapeutic Support: Therapy, whether individual or group-based, offers a structured and supportive environment to explore and address the underlying issues contributing to depression. Therapists employ evidence-based approaches to help individuals develop coping strategies, improve self-awareness, and navigate challenges. Meditation can complement these therapeutic interventions, enhancing their effectiveness.
Medication Management: In some cases, medication may be a crucial component of depression treatment. Psychiatrists are specialized in prescribing and managing medications, ensuring they are appropriate, safe, and effective. Meditation can work synergistically with medication, promoting overall well-being and potentially reducing the need for higher medication doses.
Addressing Co-Occurring Conditions: Individuals with depression may also experience co-occurring conditions such as anxiety, trauma, or substance use disorders. Mental health professionals are equipped to identify and address these complex interconnections, providing integrated care that goes beyond the surface symptoms of depression.
Crisis Intervention and Support: In moments of crisis, professional mental health support is essential. Mental health professionals can provide immediate intervention, crisis management, and a safe space for individuals experiencing acute distress. Combining meditation with professional backing ensures a comprehensive safety net during challenging times.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Strategies: Depression is a dynamic condition, and its management may require adjustments to the treatment plan over time. Mental health professionals can closely monitor your progress, assess the effectiveness of interventions, and make necessary adjustments. This ongoing support is vital for long-term well-being.
Educating and Empowering Individuals: Professionals in the mental health field play a crucial role in educating individuals about depression, its nature, and effective coping strategies. They empower individuals with knowledge and skills to navigate their mental health journey, fostering a sense of autonomy and control over their well-being.
Holistic Approach to Well-Being: Combining meditation with professional guidance provides a holistic approach to well-being. Meditation contributes to stress reduction, emotional regulation, and enhanced self-awareness, complementing the therapeutic and medical aspects of depression management.
While meditation offers valuable benefits for mental health, it is most effective when integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes professional guidance. Seeking the expertise of mental health professionals ensures a thorough understanding of your mental health, targeted interventions, and ongoing support on your journey towards healing and recovery.

The long-term benefits of meditation practice in maintaining mental well-being
With its roots deeply embedded in ancient traditions, meditation has emerged as a contemporary practice with profound implications for mental well-being. Beyond its immediate calming effects, regular meditation offers a spectrum of long-term benefits contributing to sustained mental health. Here are vital aspects of how meditation fosters enduring well-being:
Stress Resilience: One of the enduring benefits of meditation is its ability to build stress resilience. Through practices like mindfulness meditation, individuals develop a heightened awareness of stressors and learn to respond with composure rather than reactivity. Over time, this cultivates a deep-seated resilience, enabling individuals to navigate life’s challenges more easily.
Emotional Regulation: Meditation serves as a powerful tool for enhancing emotional regulation. By regularly engaging in mindfulness practices, individuals develop the capacity to observe and understand their emotions without being overwhelmed. This heightened emotional intelligence contributes to stable mood states and the ability to manage emotional fluctuations effectively.
Cognitive Flexibility: Meditation, particularly mindfulness, has been associated with improved cognitive flexibility. This refers to the ability to adapt one’s thinking and shift perspectives. Enhanced cognitive flexibility is instrumental in problem-solving, decision-making, and navigating complex situations, all of which are integral to maintaining mental well-being.
Improved Concentration and Attention: Meditation, emphasizing sustained attention, sharpens concentration over time. Through practices like focused attention meditation, individuals learn to anchor their attention on the present moment, fostering a heightened capacity for sustained focus. Improved concentration translates into increased productivity and a more engaged, current life experience.
Enhanced Self-Awareness: Regular meditation deepens self-awareness, allowing individuals to explore the landscape of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. This introspective awareness is a cornerstone of mental well-being, as it enables individuals to make conscious choices aligned with their values, leading to a more authentic and fulfilling life.
Quality of Sleep: Sleep is foundational to mental health, and meditation has been linked to improved sleep quality. Practices that induce relaxation and mindfulness contribute to a calm state of mind, making it easier for individuals to transition into restful sleep. Over time, improved sleep patterns positively impact overall mental well-being.
Brain Plasticity and Reshaping: Neuroscientific studies suggest meditation can induce brain structure and function changes. This phenomenon, known as neuroplasticity, implies that the brain can adapt and reorganize based on experiences. Regular meditation is associated with alterations in areas of the brain linked to emotional regulation, stress response, and self-awareness, contributing to long-term mental resilience.
Aging and Cognitive Decline: There is growing evidence that meditation may slow the brain’s aging process and mitigate cognitive decline associated with aging. The neuroprotective effects of meditation may contribute to sustained cognitive function, supporting mental well-being throughout the lifespan.
Increased Mindfulness in Daily Life: The essence of meditation lies in cultivating mindfulness—the practice of being fully present in the moment. Over time, individuals find that the benefits of mindfulness extend beyond formal meditation sessions into daily life. Increased mindfulness fosters a richer, more meaningful experience of each moment and enhances overall mental well-being.
Community and Connection: Many meditation practices emphasize a sense of interconnectedness and compassion. Meditation communities or group practices can foster a sense of belonging and connection. Social support and a sense of community contribute significantly to mental well-being over the long term.
The enduring benefits of meditation practice underscore its significance as a proactive approach to maintaining mental well-being. Beyond the immediate sense of calm, regular meditation shapes the mind in ways that promote resilience, emotional balance, cognitive agility, and a profound connection to the present moment—all of which are vital components of enduring mental health.
Conclusion: Harnessing the power of meditation to overcome depression
In conclusion, harnessing the power of meditation proves to be a transformative and holistic approach to overcoming depression. By delving into the intricacies of the mind and fostering stress resilience, emotional regulation, and self-awareness, meditation offers a profound complement to traditional therapeutic interventions. Its long-term benefits, ranging from enhanced cognitive flexibility to improved sleep quality, underscore its potential as a sustainable tool for mental well-being.
However, it is crucial to emphasize that while meditation can be a valuable component of a comprehensive approach to depression, seeking professional guidance remains essential. Integrating meditation into a structured treatment plan, alongside therapy and medication when needed, provides a synergistic and effective strategy for individuals on the path to healing and recovery.







