Discover the Depths of Spirituality in Islam
Spirituality is a crucial and deep aspect of Islam’s faith, surpassing all rituals and religious practices to Discover the Depths of Spirituality in Islam, unveiling hidden insights. It refers to a private deep reference to Allah, continual self-overhauling, and the pursuit of peace. For many, this level of spirituality enhances their faith and offers meaning and calm in normal life.
We shall see what is relevant to spirituality in Islam, speak about everyday practices that develop non-secular development, and learn more about Islamic mystical traditions, including Sufism. We will mirror the moral and ethical concerns that underpin spirituality, the concept of Tazkiyah or purification of souls, and how spirituality can come alive in the day-to-day. Finally, we shall gift modern-day challenges to religious nicely-being and suggest how to conquer them.
Spirituality in Islam:
Spirituality is deep and private acquaintance with Allah, cultivated via religion, worship, and a righteous way of life. It means drawing closer to Allah, purifying one’s heart and soul, and attaining that kingdom of Ihsan in which one discharges duty as though he sees Allah, even though he no longer sees Him, knowing completely that He sees him. It is a continuous procedure of self-overhauling, self-awareness, and willpower to dwell and appear at the real worth as given via the Quran and the Sunnah.
Religious Practices and Spirituality
The Five Pillars, Shahada, Salah, Zakat, Sawm, and Hajj, are religious practices instituted in Islam to represent the fundamental acts of worship each Muslim needs to consider. They preserve important structural and disciplinary capabilities for the religion. However, spirituality is something greater than this. It is concerned more with internal revel in purposes, emotions, and mind, which are expressed and skilled by a man during those rituals.

Religious practices are the outer manifestations of religion, and spirituality is the means and depth of the practices themselves. Thus, creating a Salah is an engagement of the frame, but the spirituality, therefore, connotes that one has to make a Salah with an easy intention at the back of it, attention, and a feeling within the heart for God. Similarly, fasting throughout Ramadan permits those fasting now not only to surrender eating and ingesting but also to gather strength of will, emotions of compassion, and gratitude.
Essentially, spirituality in Islam expresses the outward acts of worship, personalizing them to lead them to significance, and accordingly commencing an avenue that sustains a better relationship with Allah and eventually leads one to live an extra complete and balanced existence.
Spirituality Unveiling Hidden Insights
Tawhid (Oneness of Allah)
Tawhid is the ‘essential doctrine’ in Islam, meaning the oneness of Allah. It asserts that Allah is one, solitary, and has no friends or opposite numbers. This belief forms the basis of a Muslim’s non-secular perspective, and it needs the narration of Allah’s very best authority over humans and the preservation of all kinds of worship for Him.
This means Tawhid isn’t always a few forms of a theorem of theology; it is, however, the major impetus that objectives a Muslim’s mind, movements, and sports. It instills a feeling inside man of accountability and devotion, urges the believer to set his life by Allah’s will, and subordinate all movements to His delight.
Importance of Iman (Faith)
Iman, or faith, forms the center of a Muslim’s non-secular existence. It supplies faith inside the six articles: God, angels, discovered books, prophets, the Day of Judgment, and divine preordination. Iman, therefore, is going past mere intellectual assent and speaks of deep-seated consideration and dedication, which have to impel a Muslim to righteous and ethical living. Inner peace comes from bolstered Iman, for one is prepared to face all of existence’s difficulties confidently, and one becomes dispatched to earth for the motive.
Role of the Quran and Hadith in Spiritual Growth
For each Muslim, the holy book of Islam, the Quran, and the Hadith, the recorded sayings and movements of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) are the guiding concepts for the religious boom. The Holy Quran is, in truth, the word of God guiding, full of understanding, and the generator of righteous residing. Reciting it and studying it frequently facilitates gleaning a great deal from Allah’s will and, therefore, promotes nearness to the most exalted Allah. The Quran does now not exclude anything in life, elaborating on morality, ethics, and spirituality; consequently, it represents a complete guide to private and spiritual development.
The Hadith supplements the Quran through examples of the way to observe it. Prophet Muhammad’s (PBUH) existence is an instance of an extremely good person and determination to Allah, explaining how a man is to live through the concepts contained therein. Hadith observation allows Muslims to recognize the conditions in which some of the revelations inside the Quran occurred. It enables them to follow the best examples that had been provided using the Prophet. The Quran and Hadith offer a wealthy and holistic basis for elevating one’s spirituality onto the path of faith, virtue, and inner peace.
Daily Practices that Enhance Spirituality
The Five Pillars of Islam: The five pillars of Islam are the basics of acts of worship for Muslims and, as such, constitute the muse of a Muslim’s religion and practice. Each of these has profound religious importance for Muslims in the direction of Allah during their adventure.
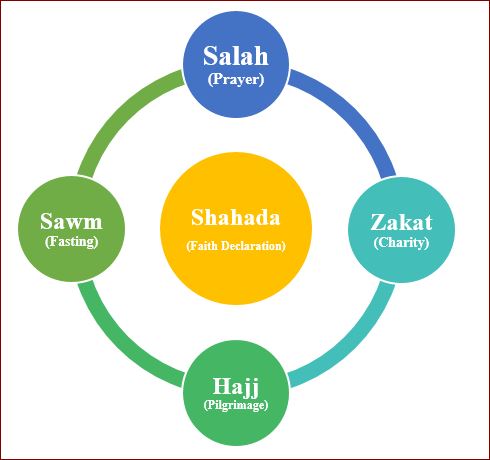
- Shahada (Faith Declaration): There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is His Messenger, PBUH. This simple announcement confirms a believer’s monotheism and that Muhammad became the remaining prophet. Shahda is the natural access factor into Islam, wherein it anchors all the spiritual lifestyles in step with a Muslim into these central tenets of the religion. It reminds one of his dedication to the direction of God and His teachings, through which a sense of direction and reason starts to be born.
- Sawm (Fasting): Sawm is fasting in Ramadan, a profound spiritual exercise with the aid of which Muslims deny their natural meals, drink, and other such crucial sundries from dawn to sunset. Fasting builds strength of mind, gratitude for what one has, and considering less lucky individuals. This allows time for reflection, more devotion, and community bonding. The act of fasting places a Muslim on the conclusion of his or her dependence on God and turns her or him more toward a non-secular boom.
- Salah (Prayer): Salah, or the five-day prayers, is one of Islamic spirituality’s primary expressions. Conducted at set times every day, they regularly remind the player about the presence of God. Salah is a bodily act, completed with recitation from the Quran and different private supplications. Doing so may nurture discipline and mindfulness and foster an instantaneous relationship between oneself and Allah. The pause to wish lets in for correcting mental and behavioral orientation and returning to peace and solace in talking with Allah.
- Zakat (Charity): Zakat is the obligation of giving a sure component of one’s wealth to the terrible. It is a method that, by giving alms, a person purifies his or her wealth and fosters an experience of social obligation or feeling. Thus, Zakat isn’t merely a monetary transaction; it is a religious transaction wherein Muslims are made to consider what Allah has bestowed and proportion it with others. By so doing, Zakat would foster generosity and entrench attention for the wider network of society and closer to Allah.
- Hajj (Pilgrimage): Hajj is the visit that should be made at least as soon as in entire life to Mecca by each Muslim if one is bodily and economically able. During the pilgrimage, a collection of acts is executed to commemorate the movements of the prophet Ibrahim and his circle of relatives. Hajj appears to be the best act of worship and submission to God. It is an effective, non-secular pilgrimage that unites, melds, and makes every single Muslim across the globe equal. This more intimate and introspective undertaking of Hajj frequently results in a large inner persona and religious revolution.
Sufism and Spirituality in Islam
Sufism Significance: Sufism is usually identified as Islam’s inner, mystical face. It targets a greater intimate and personal reference to God through those spiritual practices. It based its emergence on the early centuries of Islam as a response to the increasing materialism and formalism within the devoted. The Sufis emphasized inner purity, spiritual enlightenment, direct enjoyment of the Divine, and readability of inner notions. In due direction, Sufism evolved right into a wealthy diversity of lifestyle, with diverse orders (tariqas) and practices that continue to be ultra-modern and have an effect on the religious lives of Muslims all over the international.
Key Practices in Sufism
Dhikr (Remembrance of Allah): The remembrance of God is the cardinal and valuable factor of Sufi practice. It entails repeated recitation or chanting of the names and attributes of God, supposed to result in a heightened nation of non-secular focus and closeness to God. Dhikr can be practiced alone or in corporations. Way that rhythmic physical moves or patterns of respiration should additionally be used to awareness of the mind and the spirit.
Sufi Poetry and Music: Sufi poetry and music are crucial to Sufism. Great Sufi poets like Rumi, Hafiz, and Ibn Arabi have composed literature in-depth on divine love, solidarity, and the soul’s adventure lower back to God. Many of the poems used metaphors or allegories to face deep religious truths. Sufi tune is integrated into Sufi gatherings. Specifically, it involves appearing determination songs referred to as qawwalis, and ‘listening’ referred to as coma. The poetry and the track might also elevate the soul and the spirit in this sort of way to provide an immediate revelation of being inside the Presence of Allah.
Discover the Depths of Spirituality in Islam
Jalaluddin Rumi: Jalaluddin Rumi is one of the most famous Sufi poets whose works have transcended the limits of cultures and faith. He’s discussed the transformational nature of affection and the soul’s desire to emerge as one with Allah. Rumi additionally based the Mevlevi Sufi order of dervishes, Whirlers who spin in dance, dropping themselves in meditation as a form of worship.
Al-Ghazali: Al-Ghazali became one of the finest Muslim thinkers and mystics whose works acted as a bridge between Islamic regulation and Sufism. What he did in his seminal e-book, “The Revival of the Religious Sciences,” changed into pointing out the want for cleansing the coronary heart and emphasizing the internal dimensions of acts of worship.
Ibn Arabi: He is considered the “Greatest Master” in Sufism, and most of his large works are centered on complex metaphysical principles and unity in life. His works have deeply stimulated Islamic notions and mysticism.
Rabia al-Adawiyya: Rabia al-Adawiyya is the earliest female Sufi saint and remains remembered for her deep love for God and her mind on divine love. Her life and teachings consciousness on loving Allah for His very own sake, with no preference for paradise or fear of hell.
Added to this prolonged and unidentified list are several others who’ve contributed in the direction of enhancing Sufi spirituality. Their teaching and practices convey the Muslims toward God, pointing closer to a deeper, greater intimate quest stressing inner conversion and the mild of the heart.
Conclusion:
It is through an exploration of the non-secular intensity of Islam that we realize simply how religion and self-illuminations are intertwined. It tiers from the very essential idea of Tawhid, which asserts the solidarity of Allah, to the practical elements of Islam: Salah, Zakat, and Sawm means making up the roadmap through which a spiritual route to peace and achievement is reached.
Sufism emphasizes Dhikr, whilst poetry and song brighten up it with a special ‘prism’ through which religious experiences of human beings will be deepened and wished to be close to the Divine. Figures like Rumi, Al-Ghazali, and Rabia al-Adawiyya have attributed the height of religious devotion, inspiring generations to seek the presence of God in every walk of existence.
As you bloom, in addition to your very own religious manner of being a Muslim, we inspire you to embody those training more fully and discover an enhancement of ordinary practices that deliver meaning to faith. Whether in prayers, charity, or non-public reflection, every act brings the soul to the heart of Islamic spirituality.
Share your thoughts and the stories you can have regarding this religious path. How did you turn into an Islamic non-secular life part of your very own? Which practices resonated with you the most? Your insights can inspire others, growing a community of shared mastering and boom.
References and Further Reading
The following books, articles, and sources are encouraged to analyze for those who desire to delve deeper into the religious dimensions of Islam.
Books:
- “The Glorious Qur’an” Translated by Muhammad Tahir-ul-Qadri.
- “The Revival of the Religious Sciences” by Al-Ghazali.
- “The Conference of the Birds” by Farid ud-Din Attar.
- ” The Masnavi of Rumi” Translated by E.H. Whinfield.







